Technology
Blog on Six Degrees of Freedom
Six Degrees of Freedom Blog
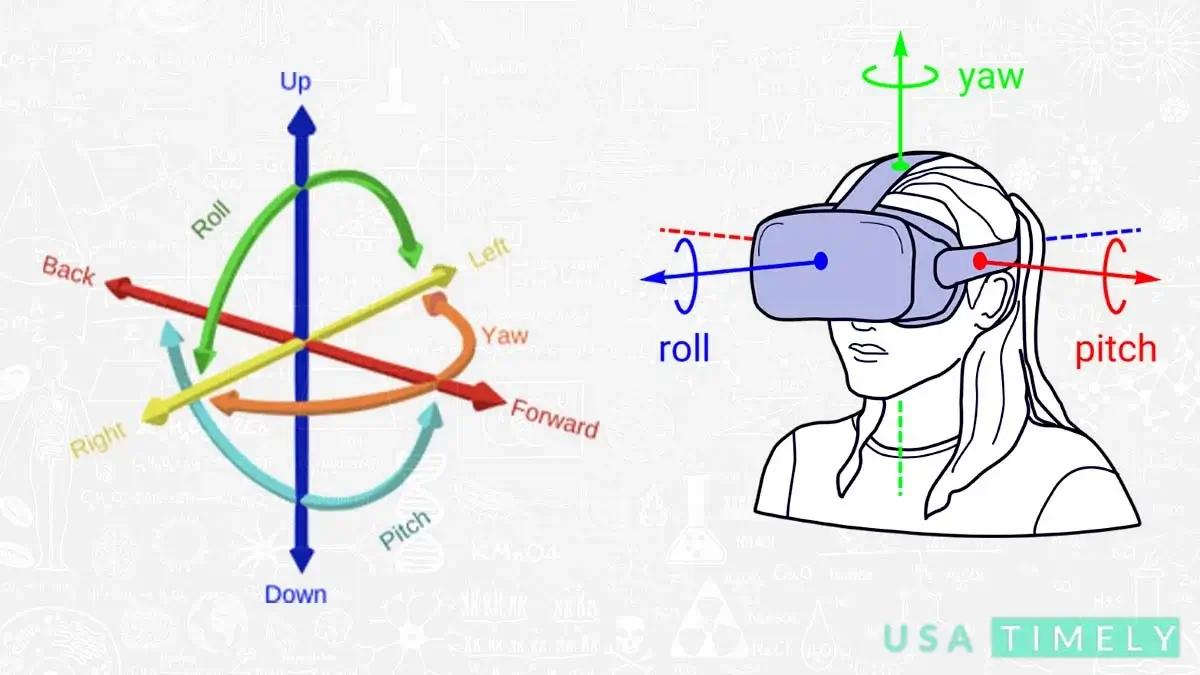
Six degrees of freedom blog (6DOF) describe the freedom of movement of a solid object in three-dimensional space. Imagine it like this: the object can move forward and backward (surge), up and down (heave), and left and right (sway) along three different axes. Additionally, it can change its orientation by rotating about three perpendicular axes – yaw (like turning your head), pitch (tilting forward or backward), and roll (tilting side to side).
On the other hand, when we talk about three degrees of freedom (3DOF), especially in the context of virtual reality, we’re focusing on tracking rotational motion only. It’s like keeping tabs on the pitch (nodding up and down), yaw (turning side to side), and roll (tilting left or right). So, in simpler terms, 6DOF allows movement in all directions, while 3DOF concentrates on tracking the object’s rotations.
Six Degrees of Freedom in Robotics
When it comes to robotics, the design of serial and parallel manipulator systems revolves around positioning an end-effector with six degrees of freedom. This means three degrees in translation, allowing movement forward/backward (surge), left/right (sway), and up/down (heave). Additionally, three degrees in orientation enable rotation around perpendicular axes – yaw (turning left/right), pitch (tilting forward/backward), and roll (tilting side to side). This design establishes a direct link between actuator positions and the manipulator’s configuration, defining its forward and inverse kinematics.
Degrees of Freedom in Robotic Arms
Describing robot arms involves specifying their degrees of freedom. This practical metric goes beyond the abstract definition and provides a tangible measure of the system’s positioning capability. For instance, in 2007, Dean Kamen, known for inventing the Segway, introduced a prototype robotic arm with an impressive 14 degrees of freedom for DARPA. Humanoid robots take it to the next level, typically featuring 30 or more degrees of freedom. Each arm has six degrees of freedom, while legs contribute five or six, and additional degrees are present in the torso and neck.
Engineering: Analyzing Mechanical Systems
In engineering, especially in the realm of biomechanical systems, understanding and measuring all six degrees of freedom is crucial. This is particularly pertinent for systems where properties need to be thoroughly analyzed. Today, the measurement of these degrees of freedom is achieved through sensors utilizing AC and DC magnetic or electromagnetic fields. These sensors transmit positional and angular data to a processing unit, and relevant software integrates this data based on user needs and programming.
Mnemonics for Angle Names: Breaking Down Movements
Breaking down the six degrees of freedom, they are categorized into two motional classes – translational and rotational envelopes.
Translational Envelopes
- Moving forward and backward on the X-axis (Surge).
- Moving left and right on the Y-axis (Sway).
- Moving up and down on the Z-axis (Heave).
Rotational Envelopes
- Tilting side to side on the X-axis (Roll).
- Tilting forward and backward on the Y-axis (Pitch).
- Turning left and right on the Z-axis (Yaw).
Understanding Rotational Envelopes in Virtual Reality Headsets
For virtual reality headsets, these rotational envelopes translate into user-friendly terms:
- Pitch: Nodding “yes”
- Yaw: Shaking “no”
- Roll: Bobbling from side to side
The Blogs Operational Envelopes in Six Degrees of Freedom
When we get into this realm of six degrees of freedom blog, there are three distinctive types of operational envelopes: Direct, Semi-direct (conditional), and Non-direct. These classifications are irrespective of factors like the remaining time for maneuver execution, the energy available, and whether the motion is commanded by a biological entity (such as a human), a robotical entity (like a computer), or a combination of both.
Direct Type: Straightforward Commands
The Direct type involves a degree that can be directly commanded without any specific conditions. It’s essentially considered a normal operation. Think of the aileron on a basic airplane – it can be controlled straightforwardly without the need for specific conditions.
Semi-direct Type: Conditions Apply
Moving on to the Semi-direct type, this involves a degree that can be commanded but under specific conditions. Consider the reverse thrust on an aircraft – it can be initiated, but certain conditions must be met before it can be effectively employed.
Non-direct Type: Environment Interaction
The Non-direct type is a bit different. It involves a degree that is achieved through interaction with the environment and cannot be directly commanded. Picture the pitching motion of a vessel at sea – it responds to the sea conditions, and you can’t simply command it to pitch without the influence of the surroundings.
Transitional Type: Adapting to the Situation
In some vehicles, there’s also a Transitional type. Take the example of the Space Shuttle. When operating in low Earth orbit, it was described as fully-direct-six because in the vacuum of space, all six degrees of freedom could be commanded via reaction wheels and RCS thrusters. However, as the Space Shuttle descended through Earth’s atmosphere for its return, the fully-direct-six degrees were no longer applicable. In this phase, it glided through the air, utilizing its wings and control surfaces for navigation.
Exploring Six Degrees of Freedom in Video Game Controllers
First-Person Shooter Games: Five Degrees of Freedom
In the realm of video games, six degrees of freedom is a term that signifies movement during gameplay. In the popular first-person shooter (FPS) genre, games typically offer five degrees of freedom. This includes moving forwards/backwards, sliding left/right, going up/down (for actions like jumping, crouching, or lying down), and the ability to yaw (turn left/right) and pitch (look up/down). Some games introduce a sixth degree of freedom if they allow leaning control, though this interpretation isn’t universally agreed upon, as leaning is seen as a limited partial rotation.
Diverse Interpretations of 6DOF in Games
The term 6DOF has been used loosely in the gaming world to describe titles that provide freedom of movement but may not precisely meet the full 6DOF criteria. Games like Dead Space 2, Homeworld, and Zone Of The Enders allow some freedom of movement, but not necessarily across all six degrees of freedom.
Examples of True 6DOF Games
True 6DOF games offer independent control of all three movement axes and all three rotational axes. Examples of these include titles such as Elite Dangerous, Shattered Horizon, the Descent franchise, Everspace, Retrovirus, Miner Wars, Space Engineers, Forsaken, and Overload. The space MMO Vendetta Online also falls into this category, providing players with a complete six degrees of freedom gaming experience.
Motion Tracking Hardware for 6DOF Head Tracking
For a more immersive gaming experience, motion tracking hardware devices like TrackIR and software-based apps such as Eyeware Beam are used for 6DOF head tracking. These technologies find their place in flight simulators and other vehicle simulators, allowing players to look around the cockpit to locate enemies or avoid in-game accidents.
3DOF and Innovative Controllers
The acronym 3DOF, denoting movement in the three dimensions but not rotation, is encountered in gaming contexts. Innovative controllers, like the Razer Hydra for PC, track both position and rotation, providing six degrees of freedom on each hand. Older devices, such as the SpaceOrb 360, and modern counterparts like the 3Dconnexion controllers, are designed for professional CAD industries.
Cutting-Edge Technology: HTC VIVE Controllers
HTC VIVE controllers represent cutting-edge technology, providing 6DOF information through lighthouse tracking that employs Time of Flight (TOF) technology to precisely determine the position of controllers in the gaming space.
FAQs About Six Degrees of Freedom Blog
What is Six Degrees of Freedom in simple terms?
6DOF stands for six degrees of freedom, describing the complete freedom of movement for an object in three-dimensional space. It includes translation along three axes (forward/backward, up/down, left/right) and rotation around three perpendicular axes (yaw, pitch, roll).
How does Six Degrees of Freedom apply to robotics?
In robotics, 6DOF is crucial for manipulator systems, providing three degrees in translation and three in orientation. This allows precise positioning of an end-effector, linking actuator positions to the manipulator’s configuration.
What are the true 6DOF games in the gaming world?
True 6DOF games allow independent control of all movement and rotational axes. Examples include Elite Dangerous, Shattered Horizon, the Descent franchise, Everspace, Retrovirus, Miner Wars, Space Engineers, Forsaken, and Overload.
How is 6DOF used in virtual reality headsets?
In virtual reality, 6DOF enables users to have immersive experiences by providing freedom of movement and rotation. Rotational envelopes translate into user-friendly actions like nodding for pitch, shaking for yaw, and bobbling for roll.
What are some motion tracking devices for 6DOF head tracking?
Devices like TrackIR and software apps like Eyeware Beam enhance gaming experiences by offering 6DOF head tracking. These find applications in flight simulators and vehicle simulators for better in-game awareness.
Which innovative controllers provide Six Degrees of Freedom on each hand?
Controllers like the Razer Hydra for PC track both position and rotation, offering six degrees of freedom on each hand. These controllers, along with modern counterparts like 3Dconnexion devices, are designed for professional CAD industries.
Final Words
In the dynamic landscape of technology, Six Degrees of Freedom (6DOF) emerges as the key to boundless movement. From robotics shaping precision to immersive gaming experiences, and the virtual reality realm expanding our perceptions, 6DOF is the bridge to freedom in all dimensions. As we navigate through these realms, the future promises even more innovative applications, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the fascinating world of six degrees of freedom.













