Technology
Blog on Six Degrees of Freedom
Six Degrees of Freedom Blog
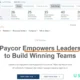
Six degrees of freedom blog (6DOF) describe the freedom of movement of a solid object in three-dimensional space. Imagine it like this: the object can move forward and backward (surge), up and down (heave), and left and right (sway) along three different axes. Additionally, it can change its orientation by rotating about three perpendicular axes – yaw (like turning your head), pitch (tilting forward or backward), and roll (tilting side to side).
On the other hand, when we talk about three degrees of freedom (3DOF), especially in the context of virtual reality, we’re focusing on tracking rotational motion only. It’s like keeping tabs on the pitch (nodding up and down), yaw (turning side to side), and roll (tilting left or right). So, in simpler terms, 6DOF allows movement in all directions, while 3DOF concentrates on tracking the object’s rotations.
Six Degrees of Freedom in Robotics
When it comes to robotics, the design of serial and parallel manipulator systems revolves around positioning an end-effector with six degrees of freedom. This means three degrees in translation, allowing movement forward/backward (surge), left/right (sway), and up/down (heave). Additionally, three degrees in orientation enable rotation around perpendicular axes – yaw (turning left/right), pitch (tilting forward/backward), and roll (tilting side to side). This design establishes a direct link between actuator positions and the manipulator’s configuration, defining its forward and inverse kinematics.
Degrees of Freedom in Robotic Arms
Describing robot arms involves specifying their degrees of freedom. This practical metric goes beyond the abstract definition and provides a tangible measure of the system’s positioning capability. For instance, in 2007, Dean Kamen, known for inventing the Segway, introduced a prototype robotic arm with an impressive 14 degrees of freedom for DARPA. Humanoid robots take it to the next level, typically featuring 30 or more degrees of freedom. Each arm has six degrees of freedom, while legs contribute five or six, and additional degrees are present in the torso and neck.
Engineering: Analyzing Mechanical Systems
In engineering, especially in the realm of biomechanical systems, understanding and measuring all six degrees of freedom is crucial. This is particularly pertinent for systems where properties need to be thoroughly analyzed. Today, the measurement of these degrees of freedom is achieved through sensors utilizing AC and DC magnetic or electromagnetic fields. These sensors transmit positional and angular data to a processing unit, and relevant software integrates this data based on user needs and programming.
Mnemonics for Angle Names: Breaking Down Movements
Breaking down the six degrees of freedom, they are categorized into two motional classes – translational and rotational envelopes.
Translational Envelopes
- Moving forward and backward on the X-axis (Surge).
- Moving left and right on the Y-axis (Sway).
- Moving up and down on the Z-axis (Heave).
Rotational Envelopes
- Tilting side to side on the X-axis (Roll).
- Tilting forward and backward on the Y-axis (Pitch).
- Turning left and right on the Z-axis (Yaw).
Understanding Rotational Envelopes in Virtual Reality Headsets
For virtual reality headsets, these rotational envelopes translate into user-friendly terms:
- Pitch: Nodding “yes”
- Yaw: Shaking “no”
- Roll: Bobbling from side to side
The Blogs Operational Envelopes in Six Degrees of Freedom
When we get into this realm of six degrees of freedom blog, there are three distinctive types of operational envelopes: Direct, Semi-direct (conditional), and Non-direct. These classifications are irrespective of factors like the remaining time for maneuver execution, the energy available, and whether the motion is commanded by a biological entity (such as a human), a robotical entity (like a computer), or a combination of both.
Direct Type: Straightforward Commands
The Direct type involves a degree that can be directly commanded without any specific conditions. It’s essentially considered a normal operation. Think of the aileron on a basic airplane – it can be controlled straightforwardly without the need for specific conditions.
Semi-direct Type: Conditions Apply
Moving on to the Semi-direct type, this involves a degree that can be commanded but under specific conditions. Consider the reverse thrust on an aircraft – it can be initiated, but certain conditions must be met before it can be effectively employed.
Non-direct Type: Environment Interaction
The Non-direct type is a bit different. It involves a degree that is achieved through interaction with the environment and cannot be directly commanded. Picture the pitching motion of a vessel at sea – it responds to the sea conditions, and you can’t simply command it to pitch without the influence of the surroundings.
Transitional Type: Adapting to the Situation
In some vehicles, there’s also a Transitional type. Take the example of the Space Shuttle. When operating in low Earth orbit, it was described as fully-direct-six because in the vacuum of space, all six degrees of freedom could be commanded via reaction wheels and RCS thrusters. However, as the Space Shuttle descended through Earth’s atmosphere for its return, the fully-direct-six degrees were no longer applicable. In this phase, it glided through the air, utilizing its wings and control surfaces for navigation.
Exploring Six Degrees of Freedom in Video Game Controllers
First-Person Shooter Games: Five Degrees of Freedom
In the realm of video games, six degrees of freedom is a term that signifies movement during gameplay. In the popular first-person shooter (FPS) genre, games typically offer five degrees of freedom. This includes moving forwards/backwards, sliding left/right, going up/down (for actions like jumping, crouching, or lying down), and the ability to yaw (turn left/right) and pitch (look up/down). Some games introduce a sixth degree of freedom if they allow leaning control, though this interpretation isn’t universally agreed upon, as leaning is seen as a limited partial rotation.
Diverse Interpretations of 6DOF in Games
The term 6DOF has been used loosely in the gaming world to describe titles that provide freedom of movement but may not precisely meet the full 6DOF criteria. Games like Dead Space 2, Homeworld, and Zone Of The Enders allow some freedom of movement, but not necessarily across all six degrees of freedom.
Examples of True 6DOF Games
True 6DOF games offer independent control of all three movement axes and all three rotational axes. Examples of these include titles such as Elite Dangerous, Shattered Horizon, the Descent franchise, Everspace, Retrovirus, Miner Wars, Space Engineers, Forsaken, and Overload. The space MMO Vendetta Online also falls into this category, providing players with a complete six degrees of freedom gaming experience.
Motion Tracking Hardware for 6DOF Head Tracking
For a more immersive gaming experience, motion tracking hardware devices like TrackIR and software-based apps such as Eyeware Beam are used for 6DOF head tracking. These technologies find their place in flight simulators and other vehicle simulators, allowing players to look around the cockpit to locate enemies or avoid in-game accidents.
3DOF and Innovative Controllers
The acronym 3DOF, denoting movement in the three dimensions but not rotation, is encountered in gaming contexts. Innovative controllers, like the Razer Hydra for PC, track both position and rotation, providing six degrees of freedom on each hand. Older devices, such as the SpaceOrb 360, and modern counterparts like the 3Dconnexion controllers, are designed for professional CAD industries.
Cutting-Edge Technology: HTC VIVE Controllers
HTC VIVE controllers represent cutting-edge technology, providing 6DOF information through lighthouse tracking that employs Time of Flight (TOF) technology to precisely determine the position of controllers in the gaming space.
FAQs About Six Degrees of Freedom Blog
What is Six Degrees of Freedom in simple terms?
6DOF stands for six degrees of freedom, describing the complete freedom of movement for an object in three-dimensional space. It includes translation along three axes (forward/backward, up/down, left/right) and rotation around three perpendicular axes (yaw, pitch, roll).
How does Six Degrees of Freedom apply to robotics?
In robotics, 6DOF is crucial for manipulator systems, providing three degrees in translation and three in orientation. This allows precise positioning of an end-effector, linking actuator positions to the manipulator’s configuration.
What are the true 6DOF games in the gaming world?
True 6DOF games allow independent control of all movement and rotational axes. Examples include Elite Dangerous, Shattered Horizon, the Descent franchise, Everspace, Retrovirus, Miner Wars, Space Engineers, Forsaken, and Overload.
How is 6DOF used in virtual reality headsets?
In virtual reality, 6DOF enables users to have immersive experiences by providing freedom of movement and rotation. Rotational envelopes translate into user-friendly actions like nodding for pitch, shaking for yaw, and bobbling for roll.
What are some motion tracking devices for 6DOF head tracking?
Devices like TrackIR and software apps like Eyeware Beam enhance gaming experiences by offering 6DOF head tracking. These find applications in flight simulators and vehicle simulators for better in-game awareness.
Which innovative controllers provide Six Degrees of Freedom on each hand?
Controllers like the Razer Hydra for PC track both position and rotation, offering six degrees of freedom on each hand. These controllers, along with modern counterparts like 3Dconnexion devices, are designed for professional CAD industries.
Final Words
In the dynamic landscape of technology, Six Degrees of Freedom (6DOF) emerges as the key to boundless movement. From robotics shaping precision to immersive gaming experiences, and the virtual reality realm expanding our perceptions, 6DOF is the bridge to freedom in all dimensions. As we navigate through these realms, the future promises even more innovative applications, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the fascinating world of six degrees of freedom.

Technology
What is Megabyte? (MB)
What Does Megabyte (MB) Mean?
A megabyte (MB) is a unit used to measure data in digital storage, like on computers or media devices. It’s equivalent to one million bytes, which is a basic unit of digital information. In simpler terms, when you hear “megabyte,” think about a chunk of data that’s pretty big, holding a lot of information.
Explains Megabyte
A megabyte (MB) is a unit used to measure data in digital storage, like on computers or media devices. It’s equivalent to one million bytes, which is a basic unit of digital information. In simpler terms, when you hear “megabyte,” think about a chunk of data that’s pretty big, holding a lot of information.
When we talk about data, we often start with bits, which are the smallest units of data in a computer. A bit is like a tiny switch that can be either on or off, represented by the numbers 1 or 0. Eight bits make up one byte, which is a basic building block for measuring data.
Now, when we talk about megabytes, we’re talking about a lot of bytes grouped together. This measurement helps us understand how much data we’re dealing with. For example, a typical 3.5-inch floppy disk can hold about 1.44 megabytes of data.
In the world of technology, we often see megabytes used to describe things like the size of files or the speed of data transfers. For example, when you’re downloading a file from the internet, you might see the speed measured in megabytes per second (MBps). This tells you how quickly the file is being transferred to your device.
Overall, megabytes are an important way to measure and understand the amount of data we’re working within the digital world.
If you want to simplify and reduce the time required for duties like managing client accounts and tracking payments than Integremos is the best option that is designed to assist companies in better credit management and debt collection.
Frequently Asked Question
Is 1 MB equal to 1000 GB?
No, in the context of computer memory, one gigabyte (GB) is actually equal to 1,024 megabytes (MB), not 1,000 MB. This is the standard used by Microsoft Windows and many others.
Is a megabyte equal to a MB?
Yes, one megabyte (MB) is equal to 1,024 kilobytes (KB) in digital storage terms, which is approximately one million bytes.
Why is 1 MB equal to 1024 KB?
The reason for this is the difference between the binary number system (base 2) and the decimal number system (base 10). In binary, each digit represents a power of 2 (1, 2, 4, 8, 16, etc.), which is why we use 1,024 as the conversion factor between kilobytes and megabytes.
Is MB bigger?
No, the megabyte (MB) is actually smaller than the gigabyte (GB). One megabyte is equivalent to one million bytes, while one gigabyte is equivalent to one billion bytes.
Which is bigger: KB, MB, or GB?
In digital storage, the sizes go like this: a kilobyte (KB) is 1,024 bytes, a megabyte (MB) is 1,024 kilobytes, a gigabyte (GB) is 1,024 megabytes, and a terabyte (TB) is 1,024 gigabytes.
Technology
Rise and Fall of Realm Scans: Exploring Paranormal Mysteries
In the past, researchers and enthusiasts often used realm scans, also known as realm scanning or realm detection, to explore and understand the mysteries of the paranormal. These scans were believed to provide insights into other dimensions, parallel universes, and even the afterlife. However, in recent years, realm scans seem to have disappeared from public attention. What happened to realm scans? This article looks at the history of realm scans, why they are no longer popular, and what might have caused their decline.
Realm scans, once a popular tool among researchers and enthusiasts curious about the supernatural, have faded from public view in recent years. These scans were believed to reveal insights into other dimensions, parallel universes, and the afterlife, and were widely used in the past. This article explores the history of realm scans, why they have become less popular, and the reasons behind their decline.
The Rise & Popularity of Realm Scans
Origins & Methodology
Realm scans emerged as a popular phenomenon in the late 20th century, coinciding with a burgeoning interest in paranormal activities and the exploration of supernatural realms. Enthusiasts and researchers, driven by a curiosity about the unknown, employed a variety of techniques and tools to conduct these scans. Among the most commonly used were electromagnetic field detectors, EVP (Electronic Voice Phenomenon) recorders, and the assistance of psychic mediums.
Notable Cases & Public Fascination
One of the pivotal moments that contributed to the rise of realm scans was the investigation of a haunted house in Amityville, New York, during the 1970s. The Warrens, a couple renowned for their work as paranormal investigators, utilized realm scans to detect and communicate with the spirits believed to inhabit the house. This high-profile case, along with others of a similar nature, captivated the public’s imagination and sparked widespread interest in realm scans.
Influence on Popular Culture
The popularity of realm scans extended beyond the realm of serious paranormal research and into popular culture. Books, films, and television shows began to feature the concept of realm scans, further fueling public curiosity and interest. This increased exposure helped cement realm scans as a recognizable tool in the exploration of the supernatural.
Decline in Popularity
Despite their initial popularity, realm scans began to decline in visibility and usage in recent years. The reasons for this decline are multifaceted and include advancements in technology that have led to new methods of paranormal investigation, as well as a shift in public interest towards other forms of supernatural exploration.
Legacy & Continued Interest
Realm scans were once a popular tool used by researchers and enthusiasts to explore the mysteries of the supernatural world. Their rise to popularity was fueled by a growing interest in paranormal phenomena and notable cases like the Amityville haunting. However, their popularity has waned in recent years, reflecting changes in technology and shifts in public interest. Nonetheless, the legacy of realm scans persists, having left an indelible mark on the history of paranormal investigation. While realm scans may no longer be as prevalent as they once were, they continue to be a topic of fascination and intrigue for those interested in the supernatural.
The Decline of Realm Scans: Exploring the Factors Behind Their Fading Popularity
Realm scans, once a popular method for exploring the supernatural, have gradually faded from public view. This article examines the various factors that have contributed to their decline in popularity.
Lack of Scientific Evidence
One of the primary causes of the decline of realm scans is the lack of scientific evidence supporting their validity. Skeptics argue that the results obtained from these scans can be easily explained by natural phenomena or psychological factors. Without concrete scientific proof, realm scans have struggled to gain credibility among the scientific community and the general public.
Advancements in Technology
Another factor contributing to the decline of realm scans is the advancement of technology. In recent years, ghost hunting equipment such as thermal cameras, EMF meters, and motion sensors has become more accessible and affordable. These modern tools offer more tangible and measurable results compared to realm scans, making them more appealing to researchers and enthusiasts.
Shift in Popular Culture
A change in popular culture can also be linked to the reduction of realm scans. In recent years, there has been a rise in fictional portrayals of the supernatural in movies, TV shows, and other forms of media. These portrayals often depict ghost hunters and paranormal investigators using high-tech equipment to detect and communicate with spirits. While these fictional portrayals may spark interest in the paranormal, they have also contributed to a perception that realm scans are outdated or less effective compared to modern ghost hunting methods.
The decline of realm scans can be attributed to a combination of factors, including a lack of scientific evidence, advancements in technology, and a shift in popular culture. While realm scans may have been popular in the past, they have gradually been replaced by more modern and scientifically supported methods of exploring the supernatural. As technology continues to advance and our understanding of the paranormal evolves, it will be interesting to see what new methods emerge to take the place of realm scans in the world of paranormal investigation.
The Potential Future of Realm Scans: A Look Ahead
While realm scans have experienced a decline in popularity in recent years, there is still potential for their future development and use. This article explores the factors that could contribute to a resurgence of interest in realm scans and their continued relevance in the field of paranormal investigation.
Persistence of Interest in the Supernatural
Despite the waning popularity of realm scans, interest in the supernatural and the unknown remains strong. People are inherently curious about the mysteries of the universe and the possibility of realms beyond our understanding. This enduring fascination suggests that there may still be a place for realm scans in the future, as long as they can adapt to meet the evolving demands of paranormal research.
Continued Exploration by Enthusiasts
While realm scans may have lost some of their mainstream appeal, there are still dedicated individuals and organizations that are committed to exploring the paranormal. These enthusiasts continue to conduct realm scans and share their findings, contributing to the body of knowledge about the supernatural. Their efforts are crucial in keeping the practice of realm scanning alive and relevant, and they may play a key role in its potential resurgence.
Shift Towards Scientific Rigor
In recent years, there has been a notable shift towards scientific rigor in paranormal investigations. Researchers are increasingly focused on gathering concrete evidence and conducting rigorous scientific studies to validate their findings. This more critical approach to paranormal phenomena has raised the standards for what is considered credible evidence, which could benefit realm scans if they can meet these higher standards.
Potential for Resurgence
The combination of persistent interest in the supernatural, continued exploration by enthusiasts, and a shift towards scientific rigor suggests that there is potential for a resurgence of interest in realm scans. If researchers can develop methods that are supported by empirical evidence and meet the standards of scientific rigor, realm scans may once again become a valuable tool in the exploration of the supernatural.
While realm scans may have fallen out of favor in recent years, there is still potential for their future development and use. The persistence of interest in the supernatural, coupled with continued exploration by enthusiasts and a shift towards scientific rigor, suggests that realm scans may yet find a new lease on life. As technology advances and research methods evolve, the potential for a revival of realm scans remains a possibility, offering new insights into the mysteries of the supernatural world.
FAQs about Realm Scans
Are Realm Scans Scientifically Proven?
No, realm scans are not scientifically proven. The lack of empirical evidence and the inability to replicate results have made it difficult for realm scans to gain credibility in the scientific community.
Can Anyone Perform Realm Scans?
Realm scans require a certain level of expertise and knowledge in the field of paranormal investigations. Although anyone can try their hand at conducting a realm scan, it is best to seek advice from more seasoned researchers or become a member of recognized paranormal investigative teams.
Are There Documented Cases of Successful Realm Scans?
There are many anecdotal reports of successful realm scans, but there aren’t many cases that have been scientifically proven. This further contributes to the skepticism surrounding the validity of realm scans.
What Are Some Alternative Methods to Realm Scans?
Using contemporary ghost-hunting tools like thermal cameras, motion sensors, and EVP recorders is an alternative to realm scans. These instruments are well-liked by researchers and enthusiasts since they yield more concrete and quantifiable outcomes.
Can Realm Scans Be Dangerous?
There isn’t any scientific proof that realm scans are harmful. However, it is important to approach paranormal investigations with caution and respect. It is recommended to follow ethical guidelines and prioritize personal safety when conducting any form of supernatural exploration.
Final Words
Realm scans, once a popular tool used to explore the supernatural, have faded in popularity. This decline is due to several factors, including a lack of scientific evidence, advancements in technology, and a shift in popular culture. While realm scans may not be as popular as they once were, there is still potential for their future development and use. Continued interest in the supernatural, exploration by enthusiasts, and a focus on scientific rigor could lead to a resurgence of interest in realm scans. As technology evolves, realm scans may offer new insights into the mysteries of the supernatural world.
Technology
Understanding Wadware: A Guide to Cybersecurity Defense

The digital era advances rapidly with new technologies, but it also introduces constantly evolving cyber threats. One of these risks is wadware, a type of harmful software that has garnered attention recently. This article delves into wadware, explaining its origins, how it operates, and why robust cybersecurity defenses are crucial.
The Evolution of Wadware: Understanding Its Past to Combat Future Threats
Wadware, a form of malicious software, has a complex and fascinating evolutionary history. Unlike appearing suddenly, it has transformed gradually into a more advanced and dangerous threat. To effectively defend against wadware, it’s essential to comprehend its journey from modest origins to its current sophisticated state.
Origins of Wadware
Wadware roots can be traced back to the early days of computing when simple viruses and worms were first created as experiments or pranks. These early forms of malware were often benign, causing little harm beyond irritating computer users.
Rise of Sophistication
Over time, malware developers became more sophisticated, creating viruses and worms with malicious intent. These programs were designed to steal sensitive information, disrupt computer systems, or even extort money from victims.
The Emergence of Wadware
Wadware represents the latest evolution of malicious software. Unlike traditional malware, which relies on infecting individual computers, wadware is designed to spread rapidly across networks, infecting multiple devices simultaneously.
Why Understanding Wadware Matters
In today’s interconnected world, wadware poses a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Understanding its evolution can help cybersecurity professionals develop more effective strategies for detecting and mitigating these threats.
Wadware evolution from simple viruses to sophisticated threats highlights the importance of staying vigilant against cyber threats. By understanding its past, we can better prepare for future challenges and protect ourselves against these malicious attacks.
Decoding Wadware: Understanding Its Intricate Operations
Cracking the code of wadware is like solving a complex digital puzzle. This section explores the detailed techniques it uses to infiltrate systems, implant harmful payloads, and hide its presence in the digital world.
Infiltration Techniques
Wadware uses various methods to infiltrate systems, such as phishing emails, malicious attachments, and compromised websites. These methods aim to deceive users into unknowingly downloading and running the malware.
Payload Deployment
Once inside a system, wadware deploys its harmful payload. This payload can include actions like stealing sensitive information, encrypting files for ransom, or turning the infected device into a bot for future attacks.
Camouflage & Evasion
Wadware is skilled at hiding to avoid detection. It can pretend to be legitimate software or use advanced techniques to blend in with normal system processes. This makes it challenging for antivirus programs to identify.
Understanding the intricate operations of wadware helps cybersecurity professionals better defend against this evolving threat.
The Targets of Wadware: Vulnerabilities & Safeguards
Wadware is an equal-opportunity threat, targeting individuals and entities of all sizes, from everyday users to large enterprises. Creating successful defence strategies requires an understanding of why certain targets are selected.
Vulnerabilities Exploited by Wadware
Wadware preys on vulnerabilities in software and human behavior. It often exploits outdated software that hasn’t been patched against known security flaws. Additionally, wadware takes advantage of people’s tendencies to click on malicious links or download suspicious attachments.
Why Wadware Targets Everyone
Wadware targets a wide range of victims because it operates on a numbers game. The more devices it infects, the more opportunities it has to achieve its malicious goals, whether that’s stealing sensitive information, extorting money, or causing disruption.
Safeguards Against Wadware
To defend against wadware, it’s crucial to keep software up to date with the latest security patches. Additionally, users should be educated about the dangers of clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or suspicious sources. Implementing robust antivirus and cybersecurity measures can also help mitigate the risks posed by wadware.
Understanding the vulnerabilities exploited by wadware and implementing effective safeguards is essential in protecting against this pervasive threat.
Individuals & Businesses: Why Are They Targeted?
Individuals
Everyday users are often targeted by wadware due to their potential vulnerability. Many individuals lack awareness about cybersecurity practices and the value of their personal information, making them easy targets for malicious attacks. Wadware exploits this vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to personal data, such as financial information or login credentials, which can then be used for fraudulent purposes.
Small Businesses
Small businesses are frequently targeted by wadware because they often lack robust cybersecurity defenses. With limited resources and expertise, small businesses may not prioritize cybersecurity measures, making them vulnerable to attacks. Wadware sees small businesses as easy targets for infiltration, seeking to exploit weaknesses in their systems to gain access to sensitive information or disrupt operations.
Large Corporations
Large corporations are attractive targets for wadware due to the potential for high-value data breaches. These companies typically have extensive networks and valuable assets, making them lucrative targets for cybercriminals. Wadware attacks on large corporations can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences. As such, these organizations are often the focus of sophisticated and targeted wadware attacks aimed at stealing valuable data or disrupting operations.
Understanding why individuals and businesses are targeted by wadware is crucial in developing effective cybersecurity strategies. By recognizing their vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate safeguards, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves against these malicious threats.
Impact on Systems: Understanding the Risks
Compromise of Private Information
Wadware can compromise sensitive personal and financial information, putting individuals at risk of identity theft and financial loss.
Monetary Damages
Wadware attacks can result in significant financial losses for businesses, including costs associated with data recovery, legal fees, and damage to reputation.
Disruption of Operations
Attacks using malware have the potential to impede company operations, resulting in lost productivity and downtime.
Defensive Strategies: Strengthening Your Defenses
User Awareness Training
Tailoring user education to identify and steer clear of suspicious behaviours and the dangers of wadware can significantly lower the probability of successful attacks.
Antivirus Software
Wadware can be found and eliminated from your computer with the use of antivirus software that you install and update frequently.
Regular Software Updates
Keeping your software up to date with the latest security patches can help protect against vulnerabilities that wadware exploits.
You may greatly lower your risk of becoming a victim of these malicious attacks by learning why and how wadware targets people and businesses and putting in place efficient protective measures.
Exploring Prominent Wadware Variants: An In-Depth Analysis
Wadware comes in various forms, each with its own characteristics and risks. By examining prominent strains and real-world examples, we can understand the diverse nature of wadware and the threats it poses.
Notable Wadware Variants
- CryptoWadware: This variant encrypts files on infected systems and demands a ransom for decryption. It has been involved in many high-profile ransomware attacks.
- KeyloggerWadware: Designed to capture keystrokes, this variant is used to steal sensitive information like passwords and credit card details.
- BankingWadware: Targeting online banking systems, this variant aims to steal financial information and credentials for unauthorized access and fraudulent transactions.
Wadware Vs. Other Malware: A Comparative Analysis
Distinguishing wadware from other forms of malware is crucial for effective cybersecurity practices. While wadware shares similarities with viruses and trojans, it possesses unique characteristics that set it apart.
Similarities with Viruses & Trojans
Like viruses, wadware can replicate itself and spread to other systems. However, wadware does not require a host file to infect other systems, unlike viruses that need to attach themselves to executable files.
Similar to trojans, wadware often disguises itself as legitimate software to trick users into downloading and executing it. However, wadware focuses more on spreading across networks and compromising multiple devices simultaneously, whereas trojans typically aim to steal data or gain unauthorized access to systems.
Unique Characteristics of Wadware
One of the key differences is that wadware is designed to spread rapidly across networks, infecting multiple devices simultaneously. This rapid spread sets it apart from other forms of malware that may infect systems one at a time.
Additionally, wadware often incorporates advanced evasion techniques to avoid detection by antivirus software and other security measures. It can also be designed to update itself, making it more challenging to remove once it has infiltrated a system.
Understanding these distinctions is vital for implementing effective cybersecurity strategies tailored to combat wadware and protect against its unique threats.
Unique Qualities of Wadware
Stealthy Operations
Wadware is skilled at hiding its presence and activities, making it difficult to detect using traditional antivirus software.
Payload Diversity
Wadware payloads can vary widely, ranging from encrypting files for ransom to stealing sensitive information or creating backdoors for future attacks.
Targeted Attacks
Unlike some malware that spreads randomly, wadware often targets specific individuals, businesses, or industries.
Understanding the unique qualities of wadware and how they differ from other malware is essential for cybersecurity professionals to effectively protect against these evolving threats.
Legal Ramifications for Wadware Offenders: Navigating Current Laws & Regulations
Engaging in wadware activities poses significant legal risks, as authorities worldwide intensify efforts to combat cybercrime. This section examines the legal landscape, focusing on laws and regulations aimed at curbing such illicit activities.
Current Legal Framework
- Computer Fraud & Abuse Act (CFAA): Enacted in the United States, the CFAA prohibits unauthorized access to computers and networks, including activities related to wadware.
- European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The GDPR imposes strict rules on the collection and processing of personal data, with severe penalties for data breaches caused by wadware.
- Cybercrime Laws: Many countries have specific laws targeting cybercrime, including the use of wadware. While the breadth and severity of these rules vary, they all essentially seek to discourage and penalise malevolent activity.
Understanding and complying with these laws and regulations is essential for individuals and organizations to avoid legal repercussions associated with wadware activities.
Legislative Structure for Prevention
International Cooperation
Given the global nature of cybercrime, international cooperation is crucial. Treaties and agreements between countries facilitate information sharing and joint efforts to combat wadware.
Awareness & Education
Governments and organizations promote awareness and education about cybersecurity, helping individuals and businesses protect themselves from wadware attacks.
Law Enforcement Efforts
Law enforcement agencies around the world work to identify and prosecute individuals and groups involved in wadware activities, using legal tools to bring them to justice.
International cooperation, coupled with awareness and education initiatives, along with law enforcement efforts, play a vital role in preventing and combating wadware activities on a global scale.
Challenges & Future Directions
Ongoing Challenges
Despite efforts to combat wadware, challenges persist. The dynamic nature of cyber risks and the swift progress of technology necessitate the ongoing modification of legal and regulatory frameworks. Additionally, the anonymity and global reach of cybercriminals make enforcement difficult.
Future Directions
Understanding the legal framework surrounding wadware and the ongoing efforts to prevent cybercrime is crucial. Individuals and organizations can better protect themselves and contribute to a safer digital environment by staying informed and implementing cybersecurity best practices.
All-Inclusive Cybersecurity Strategies: Protecting Against Wadware Threats
User Education & Awareness
Educate users about the risks of wadware and the importance of secure practices, such as avoiding suspicious links and attachments.
Strong Password Policies
Implement and enforce strong password policies, including regular changes and the use of multi-factor authentication.
Regular Software Updates
Keep all software and operating systems up to date with the latest security patches to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Use of Antivirus & Anti-Malware Software
Install and regularly update antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and remove wadware and other malicious threats.
Network Security Measures
Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and other network security measures to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Data Encryption
Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access in the event of a wadware attack.
Incident Response Plan
Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to quickly and effectively respond to wadware attacks and minimize their impact.
By implementing these comprehensive strategies, individuals and organizations can enhance their cybersecurity defenses and protect against wadware threats.
Emerging Trends & Future Threats in Wadware
AI-Powered Wadware
Wadware is increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI) to avoid detection and adapt to security measures.
Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities
Wadware is targeting IoT devices, exploiting their often weak security measures to access networks.
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
The growth of RaaS models allows cybercriminals easy access to and deployment of ransomware, including wadware, for financial gain.
Supply Chain Attacks
Wadware attacks are targeting software supply chains, aiming to compromise widely used software and services.
By staying informed about these trends and adopting proactive cybersecurity measures, organizations can better protect themselves against wadware and other evolving cyber threats.
Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Wadware Prevention
Could artificial intelligence prove to be an effective weapon against wadware? The developments in AI-based security solutions and machine learning algorithms are examined in this section.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being used in cybersecurity to detect and prevent wadware attacks. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate the presence of wadware. AI-based security solutions can also adapt to new threats in real-time, making them more effective at preventing wadware attacks than traditional antivirus software.
Real-Life Scenarios: Insights from Wadware Victims & Cybersecurity Experts
This section features interviews and first-hand anecdotes from cybersecurity experts and wadware victims to bring the threat of wadware closer to home.
Real-life stories from wadware victims and cybersecurity experts provide valuable insights into the impact of wadware attacks and the importance of effective cybersecurity measures. These accounts can help organizations understand the risks posed by wadware and motivate them to implement robust security measures to protect against such threats.
FAQs About Wadware
Is Wadware the Same as Conventional Viruses?
Even though they are both harmful, wadware is different in that it is elusive and hidden, which makes detection more difficult.
Can Individuals Defend Themselves Against Wadware?
Yes, by adhering to cybersecurity best practices, such as utilizing dependable antivirus software and updating software, the danger can be considerably decreased.
Are Large Businesses Investing in AI-Powered Malware Protection?
Many businesses are adopting AI as a proactive defense against emerging threats like wadware.
How Can I Determine If My System Is Infected With Wadware?
Unexpected pop-ups, slow performance, and odd system behaviour are some of possible symptoms. Regular system scans can also help detect wadware.
How Do I Proceed If I Think There May Be a Wadware Attack?
Cut off your internet access right away, perform a thorough antivirus check, and get in touch with your IT department or a cybersecurity specialist.
Final Words
Wadware is a sophisticated and evolving threat in the digital world. It has evolved from simple viruses to complex malware that can cause significant harm to individuals and businesses. Understanding its origins, operations, and targets is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity strategies. By staying informed about wadware and implementing robust security measures, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves against this pervasive threat.
Technology
Exploring the Benefits of MYCSULB for Students
As technology improves, universities are finding new ways to enhance the student experience. The creation of online platforms that give students quick access to crucial materials and data is one example of this kind of innovation. California State University, Long Beach (CSULB), offers its students a comprehensive online platform called mycsulb. In this article, we will explore the benefits of using mycsulb for students, including its features, user-friendliness, and impact on academic success.
Enhancing the Academic Journey: A Deep Dive into MYCSULB
California State University, Long Beach (CSULB), strives to provide its students with a seamless academic experience through the use of innovative technology. One such innovation is the introduction of mycsulb, an online platform tailored to meet the diverse needs of its student body. This article explores the various facets of mycsulb, highlighting its features, ease of use, and impact on academic success.
Understanding MYCSULB
Mycsulb serves as a virtual gateway to a plethora of university resources, consolidating everything from class registration to financial aid information under one digital roof. This centralized hub empowers students to take control of their academic journey, offering convenience and accessibility like never before. With mycsulb, students can bid farewell to the days of juggling multiple platforms and logins, simplifying their university experience.
Features & Functionality
One of mycsulb’s standout features is its intuitive class registration system. Students can effortlessly browse available courses, check class schedules, and register for classes—all within a few clicks. This streamlined process eliminates the hassle of manual registration, allowing students to focus more on their academic pursuits.
Financial aid information is another cornerstone of mycsulb’s functionality. From checking their financial aid status to applying for aid and managing resources, students can easily stay on top of their financial obligations. This transparency fosters a sense of financial responsibility and ensures that students can make informed decisions regarding their education.
Moreover, mycsulb provides students with access to their academic records, including grades, transcripts, and degree progress. This feature enables students to monitor their academic performance and track their progress towards graduation. By keeping this information readily accessible, mycsulb empowers students to take ownership of their academic journey.
Ease of Use
A key highlight of mycsulb is its user-friendly interface. Designed with students in mind, the platform boasts an intuitive layout that makes navigating through various features a breeze. Whether students are checking their class schedule or accessing financial aid information, mycsulb ensures a seamless user experience, thereby enhancing overall satisfaction.
Impact On Academic Success
Since its implementation, mycsulb has made a significant impact on academic success at CSULB. By providing easy access to essential resources and information, the platform has empowered students to better manage their academic responsibilities. This, in turn, has resulted in improved academic performance and increased graduation rates, highlighting the platform’s efficacy in supporting student success.
Mycsulb stands as a testament to CSULB’s commitment to enhancing the student experience through innovative technology. Its comprehensive features, user-friendly interface, and positive impact on academic success make it an indispensable tool for students navigating the complexities of higher education. As technology continues to evolve, platforms like mycsulb will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of education.
Exploring the Benefits of Using MYCSULB
Convenient Access to Essential Information
Mycsulb provides a one-stop platform for students to access important information conveniently. Instead of navigating multiple websites or visiting different offices, everything is centralized in mycsulb. Whether checking their class schedule, reviewing grades, or accessing financial aid information, students can find everything they need in one place. This streamlined experience saves time and reduces the hassle of managing various sources of information.
Efficient Class Registration Process
Class registration can be daunting, especially when students compete for limited spots in popular courses. Mycsulb simplifies this process with its intuitive system. Students can search for classes, view course details, and add or drop courses with just a few clicks. This eliminates manual paperwork and reduces errors or confusion. The user-friendly interface ensures a smooth registration experience.
Facilitating Seamless Communication
Effective communication is crucial for academic success, and mycsulb provides a platform for students to interact with peers and teachers. Features like email integration, discussion boards, and group messaging make it easy to connect with instructors and classmates. This enhances collaboration, provides a platform for seeking clarification, discussing assignments, and sharing resources, improving the overall learning experience.
Access to Comprehensive Academic Records
Academic records must be kept up to date, and mycsulb provides an easy way to access and handle them. Students can access grades, transcripts, and degree progress reports directly. This helps them make informed decisions about course choices and graduation schedules, as well as stay updated about their academic standing. Easy access to academic records helps students track their progress and identify areas where they may need additional support.
Simplified Financial Aid Management
Managing financial aid can be complex, but mycsulb simplifies it by providing easy access to information. Students can view their financial assistance awards, monitor application progress, and access crucial documentation. This transparency helps students understand their financial responsibilities and make educated decisions about their education. By providing a centralized platform for managing financial aid, mycsulb helps students navigate the financial aspects of their education more effectively.
Mycsulb offers a range of benefits to students, including convenient access to information, efficient class registration, seamless communication, access to academic records, and simplified financial aid management. By leveraging the features and functionalities of mycsulb, students can enhance their academic experience and achieve greater success in their educational endeavors.
How to Use MYCSULB?
Navigating Mycsulb is straightforward, thanks to its user-friendly design. Here’s a detailed guide to help you get started:
- Accessing MYCSULB
Start by visiting the CSULB website and clicking on the Mycsulb link. You’ll reach the login page as a result.
- Logging In
Use your CSULB ID and password to log into the system. If you don’t have this information yet, reach out to the CSULB IT Help Desk for assistance.
- Exploring the Homepage
After logging in, you’ll land on the Mycsulb homepage. Here, you’ll find a variety of features and resources conveniently laid out for easy access.
- Navigating the Interface
Spend some time getting acquainted with Mycsulb various areas. You’ll find options for class registration, academic records, financial aid, and more. Each section is designed to provide you with the information and tools you need to manage your academic journey effectively.
- Using Class Registration
Mycsulb makes registering for classes simple. You can search for available courses, view detailed course information, and add or drop courses with just a few clicks. This streamlined process eliminates manual paperwork and ensures you can manage your class schedule easily.
- Accessing Academic Records
Keeping track of your academic records is crucial, and Mycsulb makes it easy. You can view your grades, transcripts, and degree progress reports directly through the platform. This information allows you to stay informed about your academic standing and make informed decisions about your course selections and graduation plans.
- Managing Financial Aid
Managing financial aid can be complex, but Mycsulb simplifies the process. You can view your financial aid awards, check the status of your applications, and access important documents related to your financial aid. This transparency helps you stay informed about your financial obligations and make informed decisions about your education.
- Getting Help
If you ever have any questions or need assistance while using mycsulb, don’t hesitate to reach out to the CSULB IT Help Desk. They are available to provide support and guidance to ensure you have a smooth and successful experience with the platform.
Mycsulb is designed to make your academic journey as smooth and efficient as possible. By following these steps and exploring the various features of the platform, you can take full advantage of everything mycsulb has to offer.
Exploring MYCSULB: FAQs
Can I Access MYCSULB from my Mobile Device?
Yes, you can access mycsulb from any device with an internet connection, including mobile devices. The platform is mobile-friendly, so just use your mobile device’s web browser to log in to the mycsulb website.
Can I Use MYCSULB After Graduating from CSULB?
While mycsulb is mainly for current CSULB students, some features may still be available to alumni. However, access to certain resources and services may be limited or restricted after graduation. For more details about alumni access to mycsulb, contact the CSULB IT Help Desk.
Is MYCSULB Secure?
Yes, Mycsulb is a secure platform that prioritizes the protection of student data. CSULB uses various security measures, including authentication procedures and encryption, to ensure the integrity and privacy of user data. It’s important for students to keep their login credentials confidential and follow best practices for online security.
Can I Access MYCSULB Off-Campus?
Yes, you can access mycsulb from anywhere with an internet connection, including off-campus locations. You can log in to mycsulb and use its features and resources whether you’re at home, at a coffee shop, or on the go.
Exist Any Other Resources That Could Aid Me in Using MYCSULB?
Absolutely! CSULB provides several resources to help students navigate mycsulb efficiently. The CSULB website offers tutorials, guides, and frequently asked questions to assist students in using the platform. Additionally, students can get assistance and have any technological questions or concerns answered by the CSULB IT Help Desk.
Final Bite
Mycsulb is a valuable online platform for CSULB students, offering easy access to important resources like class registration, financial aid information, and academic records. Its user-friendly interface and impact on academic success make it an essential tool for students navigating their educational journey.
Technology
Chicago Youth Hockey Forum: Empowering Youth

In youth hockey, Chicago is famous for being a strong presence in the sport. The city has a long history and a close community of players, coaches, and parents, making it a hub for talented young athletes. The Chicago Youth Hockey Forum is a key reason for the success of youth hockey in Chicago. It plays a vital role in supporting local hockey, positively impacting the community, and providing valuable resources for young players.
Empowering the Chicago Youth Hockey Community: The Role of the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum
Fostering Community Engagement & Support
The Chicago Youth Hockey Forum stands as a vital digital platform that unites players, parents, coaches, and enthusiasts of youth hockey in the Chicago region. It serves as a central hub for discussions, information sharing, and networking within the local hockey community, providing a vital space for individuals to connect, inquire, seek guidance, and exchange experiences related to youth hockey.
Facilitating Communication & Collaboration
At its core, the forum plays a pivotal role in facilitating communication and collaboration among diverse stakeholders in the Chicago youth hockey community. Coaches leverage the platform to share their knowledge and expertise, parents seek guidance on navigating various aspects of the sport, and players connect with peers who share their passion for hockey. This exchange of information and ideas cultivates a supportive and inclusive environment, nurturing the growth and development of young athletes.
Empowering & Educating Participants
Moreover, the forum empowers and educates its participants by providing access to a wealth of resources, including articles, videos, and expert advice, all tailored to enhance their understanding and enjoyment of Chicago youth hockey forum. Whether it’s tips on improving skills, advice on injury prevention, or guidance on balancing academics and athletics, the forum serves as a valuable repository of information for individuals at all levels of involvement in the sport.
Building a Stronger Hockey Community
By fostering a sense of community and camaraderie, the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum plays a crucial role in building a stronger and more cohesive youth hockey community in Chicago. Through its digital platform, the forum brings together individuals from diverse backgrounds and experiences, creating a rich tapestry of perspectives and insights that contribute to the overall growth and success of youth hockey in the region.
Driving Innovation & Excellence
Furthermore, the forum serves as a catalyst for innovation and excellence in Chicago youth hockey forum, inspiring participants to push the boundaries of their abilities and strive for greatness. By showcasing success stories, highlighting best practices, and promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement, the forum motivates individuals to reach their full potential and achieve their goals in the sport.
In summary, the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum plays a multifaceted role in the local youth hockey community, serving as a catalyst for communication, collaboration, empowerment, and innovation. By providing a platform for individuals to connect, learn, and grow, the forum helps build a stronger, more vibrant youth hockey community in Chicago, ensuring that the sport continues to thrive for generations to come.
Exploring the Benefits of the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum
The Chicago Youth Hockey Forum stands out as a crucial resource for the local hockey community, offering a multitude of benefits to its users. Here’s a closer look at some of the main advantages:
- Access to Expertise: One of the most significant benefits of the forum is the access it provides to expertise. Coaches and seasoned players utilize the platform to share their knowledge, insights, and tips for success in the sport. This allows young athletes to glean valuable guidance and mentorship from those who have already achieved success, paving the way for their own growth and development in the sport.
- Networking Opportunities: The forum serves as an invaluable networking tool, enabling individuals to connect with other players, parents, and coaches within the local hockey community. This networking can lead to a variety of new opportunities, such as finding a team, discovering new training programs, or even making connections that could benefit their future hockey careers. The connections made through the forum can be instrumental in helping individuals advance in their hockey journeys.
- Advice & Support: For parents, the forum offers a wealth of advice and support on various aspects of youth hockey. Whether it’s seeking guidance on finding the right equipment, managing the demands of the sport, or navigating the college recruitment process, parents can find valuable information and support from others who have been through similar experiences. This support system can be invaluable for parents who are new to the world of Chicago youth hockey forum and are looking for guidance on how best to support their young athletes.
- Community Building: Perhaps most importantly, the forum helps to foster a sense of community among young hockey players. Through the forum, players can establish connections, discover mentors, and create a network of support that extends beyond the rink. This sense of community can be incredibly motivating and can help young athletes stay engaged and committed to the sport as they pursue their hockey goals. Additionally, the sense of belonging to a community can enhance the overall experience of participating in youth hockey, making it more enjoyable and fulfilling for players of all levels.
Chicago Youth Hockey Forum plays a pivotal role in the local hockey community, offering a wide range of benefits that contribute to the growth and success of young athletes in the sport. From providing access to expertise and networking opportunities to offering advice and support, the forum serves as a valuable resource for individuals involved in youth hockey in the Chicago area.
Real-Life Impact of the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum
Supporting Chicago Youth Hockey Forum Dreams: John’s Story
John, a talented young hockey player, aspired to play college hockey but needed guidance on the recruitment process. His parents turned to the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum for help. Through the forum, they connected with experienced hockey parents who had successfully guided their children to college teams. These parents gave valuable advice on creating a standout player profile, contacting college coaches, and impressing at showcases. With this support, John secured a spot on a college hockey team, fulfilling his dream of playing at the collegiate level.
Navigating Equipment Choices: Sarah’s Experience
Sarah, a dedicated young hockey player, needed new equipment but was overwhelmed by the options. Her parents asked the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum for advice. The forum community offered a range of suggestions and reviews, helping Sarah’s parents choose the best equipment for her. This ensured that Sarah had the right gear for her performance and highlighted the forum’s supportive and knowledgeable community.
Recovering from Injury: Jack’s Journey
Jack, a promising young hockey player, faced a serious injury requiring a long recovery. During this tough time, Jack and his family found support from the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum. Forum members shared their own recovery experiences, offering advice on physical therapy, mental health, and maintaining a positive attitude. This support network helped Jack stay motivated, and he returned to the ice stronger than before.
Community Building & Support: The Forum’s Overall Impact
Beyond these individual stories, the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum has had a broader impact on the local hockey community. It has created a platform for players, parents, coaches, and enthusiasts to come together, share experiences, and support one another. This sense of community has not only enriched the hockey experience for individuals but has also contributed to the overall growth and development of youth hockey in the Chicago area.
Education & Empowerment: The Forum’s Role in Skill Development
Moreover, the forum has played a role in educating and empowering its members. Through access to expert advice, resources, and discussions, forum users have been able to enhance their knowledge and skills in various aspects of chicago youth hockey forum. This has not only benefited individual players and families but has also contributed to the overall improvement of the local hockey community.
Networking & Opportunities: The Forum as a Gateway
Additionally, the forum has served as a gateway to networking and opportunities within the hockey community. By connecting individuals with similar interests and goals, the forum has facilitated the formation of valuable connections that have led to new friendships, team placements, and other opportunities that have enriched the hockey experience for its members.
The Chicago Youth Hockey Forum has had a significant impact on the local hockey community, providing valuable support, resources, and opportunities that have helped young athletes achieve their goals and overcome challenges. Its role in fostering a sense of community, providing education and empowerment, and facilitating networking and opportunities has made it a vital resource for youth hockey players, parents, coaches, and enthusiasts in the Chicago area.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum
Is the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum exclusive to Chicago-based hockey players?
No, the forum is open to anyone interested in youth hockey, not just those in Chicago. People from other regions can also benefit from the knowledge and resources shared on the forum.
What is the Chicago Youth Hockey Forum’s membership process?
To join, visit the website and sign up for an account. Registration is free. Once you have an account, you can start participating in discussions and accessing the resources available on the forum.
Can I ask questions on the forum even if I am new to youth hockey?
Yes, the forum welcomes individuals of all experience levels. Whether you are a seasoned player, a new parent to the sport, or just curious about youth hockey, you can ask questions and seek guidance on the forum.
Are there any rules or guidelines for using the forum?
Yes, there are rules and guidelines to ensure discussions are respectful and informative. Users should familiarize themselves with these rules before participating.
Can I use this forum to promote my hockey-related services?
Yes, there are specific sections for advertising and promoting hockey-related services. If you offer coaching, training, or other services related to youth hockey, you can share information about your offerings in these sections.
In The End
Chicago Youth Hockey Forum is a valuable resource for the local hockey community, offering support, education, and networking opportunities for players, parents, coaches, and enthusiasts. It provides a platform for people to connect, share experiences, and access resources that help them improve their skills and enjoy the sport. Whether you’re new to hockey or a seasoned player, the forum welcomes everyone and is a great place to learn, connect, and grow in the world of youth hockey.
-

 Celebrity6 months ago
Celebrity6 months agoMisty Severi – The Breaking News Reporter
-

 Technology6 months ago
Technology6 months agoIntegremos, What is it? Complete Information
-

 Celebrity6 months ago
Celebrity6 months agoBeth Grosshans Husband: Robert Smith
-

 Celebrity5 months ago
Celebrity5 months agoWho is Dr. Zena Al-Adeeb?
-

 Business6 months ago
Business6 months agoBoeing Struggles For Trust Amid Quality Lapses
-

 Finance6 months ago
Finance6 months agoMerchant Cash Advance Blursoft: Rapid Business Financing
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoKorps Sukarela: Detailed Information
-

 Entertainment6 months ago
Entertainment6 months agoQuentin Tarantino and Brad Pitt Reunite for The Movie Critic