Technology
Blog on Six Degrees of Freedom
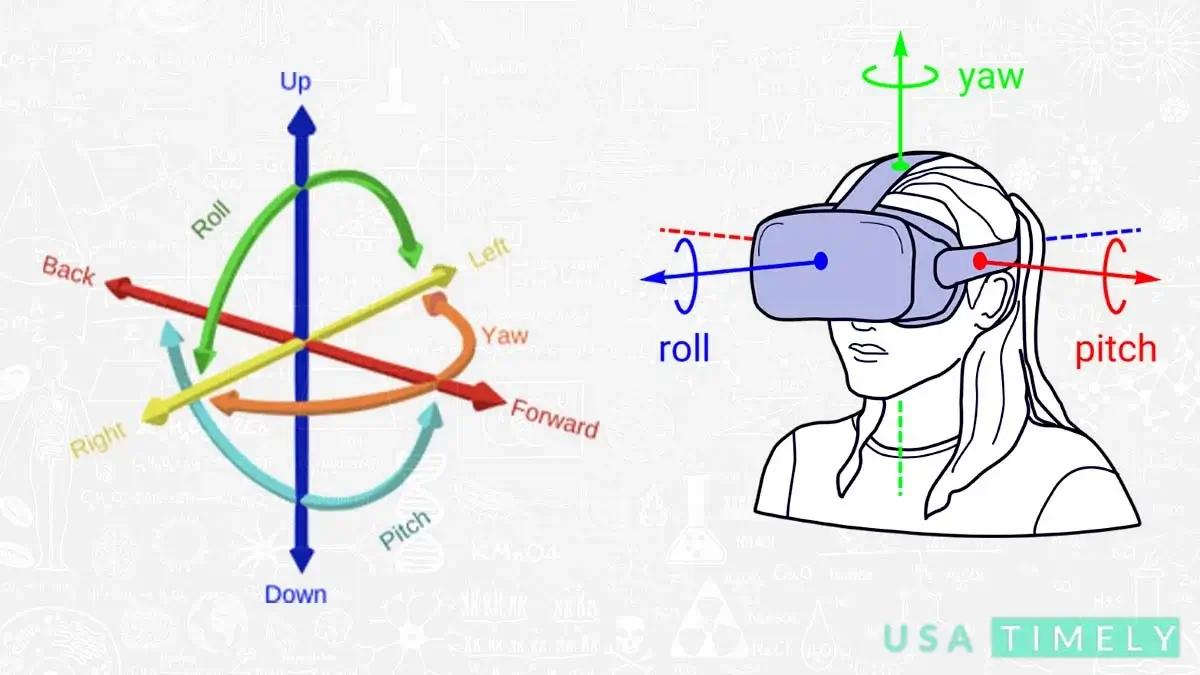
Six Degrees of Freedom Blog
Six degrees of freedom blog (6DOF) describe the freedom of movement of a solid object in three-dimensional space. Imagine it like this: the object can move forward and backward (surge), up and down (heave), and left and right (sway) along three different axes. Additionally, it can change its orientation by rotating about three perpendicular axes – yaw (like turning your head), pitch (tilting forward or backward), and roll (tilting side to side).
On the other hand, when we talk about three degrees of freedom (3DOF), especially in the context of virtual reality, we’re focusing on tracking rotational motion only. It’s like keeping tabs on the pitch (nodding up and down), yaw (turning side to side), and roll (tilting left or right). So, in simpler terms, 6DOF allows movement in all directions, while 3DOF concentrates on tracking the object’s rotations.
Six Degrees of Freedom in Robotics
When it comes to robotics, the design of serial and parallel manipulator systems revolves around positioning an end-effector with six degrees of freedom. This means three degrees in translation, allowing movement forward/backward (surge), left/right (sway), and up/down (heave). Additionally, three degrees in orientation enable rotation around perpendicular axes – yaw (turning left/right), pitch (tilting forward/backward), and roll (tilting side to side). This design establishes a direct link between actuator positions and the manipulator’s configuration, defining its forward and inverse kinematics.
Degrees of Freedom in Robotic Arms
Describing robot arms involves specifying their degrees of freedom. This practical metric goes beyond the abstract definition and provides a tangible measure of the system’s positioning capability. For instance, in 2007, Dean Kamen, known for inventing the Segway, introduced a prototype robotic arm with an impressive 14 degrees of freedom for DARPA. Humanoid robots take it to the next level, typically featuring 30 or more degrees of freedom. Each arm has six degrees of freedom, while legs contribute five or six, and additional degrees are present in the torso and neck.
Engineering: Analyzing Mechanical Systems
In engineering, especially in the realm of biomechanical systems, understanding and measuring all six degrees of freedom is crucial. This is particularly pertinent for systems where properties need to be thoroughly analyzed. Today, the measurement of these degrees of freedom is achieved through sensors utilizing AC and DC magnetic or electromagnetic fields. These sensors transmit positional and angular data to a processing unit, and relevant software integrates this data based on user needs and programming.
Mnemonics for Angle Names: Breaking Down Movements
Breaking down the six degrees of freedom, they are categorized into two motional classes – translational and rotational envelopes.
Translational Envelopes
- Moving forward and backward on the X-axis (Surge).
- Moving left and right on the Y-axis (Sway).
- Moving up and down on the Z-axis (Heave).
Rotational Envelopes
- Tilting side to side on the X-axis (Roll).
- Tilting forward and backward on the Y-axis (Pitch).
- Turning left and right on the Z-axis (Yaw).
Understanding Rotational Envelopes in Virtual Reality Headsets
For virtual reality headsets, these rotational envelopes translate into user-friendly terms:
- Pitch: Nodding “yes”
- Yaw: Shaking “no”
- Roll: Bobbling from side to side
The Blogs Operational Envelopes in Six Degrees of Freedom
When we get into this realm of six degrees of freedom blog, there are three distinctive types of operational envelopes: Direct, Semi-direct (conditional), and Non-direct. These classifications are irrespective of factors like the remaining time for maneuver execution, the energy available, and whether the motion is commanded by a biological entity (such as a human), a robotical entity (like a computer), or a combination of both.
Direct Type: Straightforward Commands
The Direct type involves a degree that can be directly commanded without any specific conditions. It’s essentially considered a normal operation. Think of the aileron on a basic airplane – it can be controlled straightforwardly without the need for specific conditions.
Semi-direct Type: Conditions Apply
Moving on to the Semi-direct type, this involves a degree that can be commanded but under specific conditions. Consider the reverse thrust on an aircraft – it can be initiated, but certain conditions must be met before it can be effectively employed.
Non-direct Type: Environment Interaction
The Non-direct type is a bit different. It involves a degree that is achieved through interaction with the environment and cannot be directly commanded. Picture the pitching motion of a vessel at sea – it responds to the sea conditions, and you can’t simply command it to pitch without the influence of the surroundings.
Transitional Type: Adapting to the Situation
In some vehicles, there’s also a Transitional type. Take the example of the Space Shuttle. When operating in low Earth orbit, it was described as fully-direct-six because in the vacuum of space, all six degrees of freedom could be commanded via reaction wheels and RCS thrusters. However, as the Space Shuttle descended through Earth’s atmosphere for its return, the fully-direct-six degrees were no longer applicable. In this phase, it glided through the air, utilizing its wings and control surfaces for navigation.
Exploring Six Degrees of Freedom in Video Game Controllers
First-Person Shooter Games: Five Degrees of Freedom
In the realm of video games, six degrees of freedom is a term that signifies movement during gameplay. In the popular first-person shooter (FPS) genre, games typically offer five degrees of freedom. This includes moving forwards/backwards, sliding left/right, going up/down (for actions like jumping, crouching, or lying down), and the ability to yaw (turn left/right) and pitch (look up/down). Some games introduce a sixth degree of freedom if they allow leaning control, though this interpretation isn’t universally agreed upon, as leaning is seen as a limited partial rotation.
Diverse Interpretations of 6DOF in Games
The term 6DOF has been used loosely in the gaming world to describe titles that provide freedom of movement but may not precisely meet the full 6DOF criteria. Games like Dead Space 2, Homeworld, and Zone Of The Enders allow some freedom of movement, but not necessarily across all six degrees of freedom.
Examples of True 6DOF Games
True 6DOF games offer independent control of all three movement axes and all three rotational axes. Examples of these include titles such as Elite Dangerous, Shattered Horizon, the Descent franchise, Everspace, Retrovirus, Miner Wars, Space Engineers, Forsaken, and Overload. The space MMO Vendetta Online also falls into this category, providing players with a complete six degrees of freedom gaming experience.
Motion Tracking Hardware for 6DOF Head Tracking
For a more immersive gaming experience, motion tracking hardware devices like TrackIR and software-based apps such as Eyeware Beam are used for 6DOF head tracking. These technologies find their place in flight simulators and other vehicle simulators, allowing players to look around the cockpit to locate enemies or avoid in-game accidents.
3DOF and Innovative Controllers
The acronym 3DOF, denoting movement in the three dimensions but not rotation, is encountered in gaming contexts. Innovative controllers, like the Razer Hydra for PC, track both position and rotation, providing six degrees of freedom on each hand. Older devices, such as the SpaceOrb 360, and modern counterparts like the 3Dconnexion controllers, are designed for professional CAD industries.
Cutting-Edge Technology: HTC VIVE Controllers
HTC VIVE controllers represent cutting-edge technology, providing 6DOF information through lighthouse tracking that employs Time of Flight (TOF) technology to precisely determine the position of controllers in the gaming space.
FAQs About Six Degrees of Freedom Blog
What is Six Degrees of Freedom in simple terms?
6DOF stands for six degrees of freedom, describing the complete freedom of movement for an object in three-dimensional space. It includes translation along three axes (forward/backward, up/down, left/right) and rotation around three perpendicular axes (yaw, pitch, roll).
How does Six Degrees of Freedom apply to robotics?
In robotics, 6DOF is crucial for manipulator systems, providing three degrees in translation and three in orientation. This allows precise positioning of an end-effector, linking actuator positions to the manipulator’s configuration.
What are the true 6DOF games in the gaming world?
True 6DOF games allow independent control of all movement and rotational axes. Examples include Elite Dangerous, Shattered Horizon, the Descent franchise, Everspace, Retrovirus, Miner Wars, Space Engineers, Forsaken, and Overload.
How is 6DOF used in virtual reality headsets?
In virtual reality, 6DOF enables users to have immersive experiences by providing freedom of movement and rotation. Rotational envelopes translate into user-friendly actions like nodding for pitch, shaking for yaw, and bobbling for roll.
What are some motion tracking devices for 6DOF head tracking?
Devices like TrackIR and software apps like Eyeware Beam enhance gaming experiences by offering 6DOF head tracking. These find applications in flight simulators and vehicle simulators for better in-game awareness.
Which innovative controllers provide Six Degrees of Freedom on each hand?
Controllers like the Razer Hydra for PC track both position and rotation, offering six degrees of freedom on each hand. These controllers, along with modern counterparts like 3Dconnexion devices, are designed for professional CAD industries.
Final Words
In the dynamic landscape of technology, Six Degrees of Freedom (6DOF) emerges as the key to boundless movement. From robotics shaping precision to immersive gaming experiences, and the virtual reality realm expanding our perceptions, 6DOF is the bridge to freedom in all dimensions. As we navigate through these realms, the future promises even more innovative applications, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the fascinating world of six degrees of freedom.

Technology
Moddroid MeChat: Everything You Need to Know
Moddroid MeChat Love Secrets: What’s Inside?
Moddroid MeChat Love Secrets is a modified version of the popular dating and storytelling game MeChat. This version unlocks hidden features, premium choices, and exclusive love storylines, allowing players to explore romantic adventures without limitations. Many users prefer this modded version to fully enjoy the interactive dating experience without restrictions.
Moddroid MeChat Latest Version: What’s New?
The Moddroid MeChat latest version comes with enhanced features, improved gameplay, and bug fixes. Updates often include new character stories, additional chat interactions, and smoother performance. Players who download the latest version from Moddroid can expect better functionality and new romantic experiences with virtual characters.
Playmods MeChat: Another Source for Modded Versions
If you’re looking for alternative modded versions of MeChat, Playmods MeChat is another popular platform. Similar to Moddroid, Playmods offers modified MeChat APKs with unlocked premium choices, giving players more freedom in their interactions and story progression.
Apkmody MeChat: Safe and Secure Mod Downloads
Apkmody MeChat is another reliable source for downloading modified versions of MeChat. Many gamers trust Apkmody because it provides safe and regularly updated mod APKs. This platform ensures that players can access premium features without worrying about security risks.
MeChat Mod APK 64 Bit: Compatibility and Features
For those using high-performance devices, the MeChat Mod APK 64 Bit version ensures smoother gameplay and better compatibility. This version is optimized for 64-bit Android devices, reducing crashes and improving graphics performance. Users who prefer an enhanced gaming experience should look for this version when downloading MeChat mods.
Freeappmods MeChat: Downloading Mods for Free
Freeappmods MeChat provides a free and accessible way to download modded versions of MeChat. It offers unlocked choices, unlimited in-game currency, and premium character interactions, making it a great option for players who want a VIP experience without paying for in-app purchases.
MeChat Download: Where to Get the Game?
For those who prefer the official version, MeChat download is available on the Google Play Store and Apple App Store. However, modded versions can be found on platforms like Moddroid, Apkmody, Playmods, and Freeappmods. Players should choose their preferred version based on whether they want an unmodified or enhanced gameplay experience.
Liteapks MeChat: A Lightweight Alternative
For players who want a smaller, more efficient version of the game, Liteapks MeChat provides a lightweight MeChat mod. This version is ideal for devices with limited storage or lower processing power, offering the same exciting interactive storytelling experience with fewer system demands.
Conclusion
Whether you’re looking for Moddroid MeChat Love Secrets, the latest version, or alternative downloads like Playmods MeChat and Apkmody MeChat, there are plenty of options available. Each version offers unique benefits, from unlocking premium choices to providing a lightweight alternative. No matter how you choose to play, MeChat continues to be an engaging and immersive dating simulation game.
Technology
Disquantified.org: Everything You Need to Know

Disquantified.org: An Overview
Disquantified.org is an emerging platform that provides insights into business information, financial records, and corporate updates. Whether you’re looking for company registration details or searching for insolvency records, this website serves as a valuable resource for individuals and businesses.
Disquantified.org People Also Search for Login
Many users looking for Disquantified.org also search for login information, likely seeking access to business data, reports, or financial records. If you’re trying to log in, ensure you’re using the official website and the correct credentials to avoid security issues.
Www.gov.uk Companies House: Official Business Records
The UK Companies House website (www.gov.uk Companies House) is the official registry for UK businesses. It provides access to company formation details, financial statements, and director information. Users interested in Disquantified.org often visit Companies House to verify business legitimacy and compliance.
Ryan Valdema: Who Is He?
Ryan Valdema is a name frequently associated with business registrations, financial records, or corporate updates. While there is limited publicly available information, searches for him often appear alongside Disquantified.org, suggesting a potential connection to business management or regulatory records.
Company Registration Search: How to Check a Business?
A company registration search is essential for verifying business legitimacy and legal status. Websites like Companies House, Disquantified.org, and Find and Update Company Information Service allow users to look up registration numbers, company directors, and financial statements before engaging in business transactions.
Https Find and Update Company Information Service Gov UK Appeal a Penalty
If a company faces penalties for late filings or non-compliance, they may need to visit Find and Update Company Information Service to appeal a penalty. This government platform provides guidance on resolving disputes related to corporate filings and maintaining compliance with UK regulations.
Voir Social Companies House: Exploring Business Networks
Voir Social Companies House is another term that frequently appears in searches related to business data. It may refer to tracking social corporate connections, partnerships, and financial dealings through Companies House records. Businesses and investors often use this feature to analyze corporate networks.
Company Update: Keeping Business Information Current
A company update is necessary for businesses to stay compliant with legal requirements. Platforms like Disquantified.org and Companies House allow companies to update their registered addresses, directors, and financial statements to maintain transparency and avoid penalties.
How Long Do You Stay on the Insolvency Register?
If a company or individual is declared insolvent, they may appear on the UK Insolvency Register. The typical duration for being listed on this register is three years, but in some cases, it can last longer depending on the severity of the financial situation and legal proceedings. Checking this register helps businesses and investors assess financial risks before entering into agreements.
Conclusion
Disquantified.org serves as a key resource for business insights, corporate compliance, and financial transparency. Whether you’re looking for company registration search options, Companies House updates, or insolvency records, this platform, along with government services like Find and Update Company Information, provides essential tools for businesses and investors.
Technology
TurboGeek.org: Exploring Popular Searches and User Queries

What Is TurboGeek.org?
TurboGeek.org is a platform that caters to tech enthusiasts, providing information on programming, development tools, and open-source communities. Many users visit the site to explore GitHub repositories, software guides, and trending tech topics.
TurboGeek.org People Ask for GitHub: Why the Connection?
One of the most frequent queries linked to TurboGeek.org is “people ask for GitHub.” Since TurboGeek focuses on technology and coding, many visitors search for:
- GitHub repositories for open-source projects
- Guides on using GitHub for version control
- GitHub alternatives and comparisons
- Troubleshooting GitHub issues
These searches indicate that users rely on TurboGeek.org for developer-friendly content related to GitHub and software management.
Ask People: How User Queries Shape Content
The “Ask People” section of search engines often provides valuable insights into trending topics. Users visiting TurboGeek.org frequently look for:
- Tech tutorials and coding tips
- Software recommendations
- Security best practices
- Tech community discussions
This highlights the demand for knowledge-sharing platforms where developers and tech enthusiasts can find answers to their most pressing questions.
People Also: How Search Trends Guide Content Creation
Search engines often include a “People Also” section, which suggests related questions based on user behavior. Common queries related to TurboGeek.org include:
- What are the best coding resources?
- How to contribute to open-source projects?
- Where to find reliable software reviews?
- How to optimize GitHub repositories for collaboration?
By analyzing these questions, content creators and developers can tailor their resources to meet user needs effectively.
Keywords People Use: Understanding Search Behavior
Knowing the keywords people use when searching for TurboGeek.org can help in optimizing content and reaching a wider audience. Some commonly searched keywords include:
- “TurboGeek GitHub repositories”
- “Best tech forums for developers”
- “TurboGeek.org software reviews”
- “Open-source project collaboration”
By leveraging these keywords, websites can improve visibility and attract a tech-savvy audience.
Conclusion
TurboGeek.org serves as a valuable hub for tech enthusiasts looking for GitHub insights, open-source projects, and coding resources. With growing search trends focusing on “People Ask,” “People Also,” and relevant keywords, the platform continues to be a go-to resource for developers and software professionals.
Technology
www.TurboGeek.org: What People Are Searching For

What Is www.TurboGeek.org?
www.TurboGeek.org is a tech-centric platform that provides insights into software development, open-source tools, operating systems, and web technologies. Many users visit this site for expert guidance on coding, troubleshooting, and optimizing their tech stacks.
www.TurboGeek.org People Also Search for Chrome
One of the most common queries linked to TurboGeek.org is “people also search for Chrome.” This suggests that users visiting the site are often looking for:
- Chrome extensions for developers
- Chrome DevTools tutorials
- Browser optimization for coding
- Troubleshooting Chrome issues for web development
Since Chrome is widely used for web development, its connection with TurboGeek.org makes sense for developers and tech enthusiasts.
www.TurboGeek.org People Also Search for Example
The phrase “people also search for example” indicates that users are looking for practical examples related to various technologies. These may include:
- Example scripts for programming languages
- Code snippets for debugging
- Configuration file samples for different software
- Best practices and templates for development
This search pattern highlights the importance of hands-on learning in tech communities.
www.TurboGeek.org People Also Search for PHP
PHP is a widely used scripting language, particularly for web development. Searches related to PHP on TurboGeek.org suggest that users are interested in:
- PHP frameworks like Laravel and CodeIgniter
- PHP security best practices
- Optimizing PHP performance
- PHP vs. other backend technologies
As an open-source programming language, PHP remains a major topic of discussion among TurboGeek.org visitors.
www.TurboGeek.org People Also Search for Ubuntu
Ubuntu, a popular Linux distribution, is frequently associated with TurboGeek.org. Related searches indicate that users are looking for:
- Ubuntu server setup and configuration
- Ubuntu vs. other Linux distributions
- How to run development environments on Ubuntu
- Troubleshooting Ubuntu installation and updates
Since many developers prefer Ubuntu for software development and server management, it’s no surprise that this topic is commonly searched alongside TurboGeek.org.
www.TurboGeek.org People Also Search for CentOS
Similar to Ubuntu, CentOS is a Linux-based operating system widely used in server environments. Searches related to CentOS on TurboGeek.org include:
- CentOS vs. Ubuntu: Which is better for servers?
- Setting up CentOS for web hosting
- CentOS security and updates
- Troubleshooting CentOS system errors
With CentOS being a stable OS for enterprise use, its relevance to TurboGeek.org is clear.
Conclusion
www.TurboGeek.org is a valuable resource for tech enthusiasts searching for insights into Chrome, PHP, Ubuntu, CentOS, and real-world coding examples. These related searches reveal that the site caters to developers, system administrators, and tech professionals looking for reliable information on software and web technologies.
Technology
Yexex.GitHub: What You Need to Know

What Is Yexex.GitHub?
Yexex.GitHub is a GitHub-based repository or project that has gained attention among developers and tech enthusiasts. It is often searched for in connection with open-source coding, programming tools, and development resources.
Why Do People Search for Yexex.GitHub?
There are several reasons why users look up Yexex.GitHub:
- Exploring repositories for coding projects
- Finding scripts or software solutions
- Looking for collaboration opportunities in open-source development
- Accessing documentation and technical guides
Since GitHub is a platform that hosts millions of projects, a specific repository like Yexex.GitHub could be relevant to developers interested in unique coding solutions.
How Yexex.GitHub Relates to Open-Source Development
GitHub is one of the most popular platforms for version control and collaboration. A repository like Yexex.GitHub can be used for:
- Sharing open-source projects with the developer community
- Hosting documentation and guides for software tools
- Tracking changes and contributions to coding projects
- Facilitating discussions through GitHub Issues and Pull Requests
This makes it an essential part of the modern software development ecosystem.
How to Use Yexex.GitHub
If you come across Yexex.GitHub, you can explore its contents by:
- Visiting GitHub and searching for the repository
- Checking the README file for details on its purpose
- Exploring different branches and commits
- Cloning or downloading the project for testing
- Contributing through Pull Requests if it’s open-source
Following these steps can help developers get involved in GitHub projects efficiently.
Conclusion
Yexex.GitHub appears to be a GitHub-based project or repository that attracts developer interest. Whether it involves coding resources, software tools, or open-source contributions, it highlights the importance of GitHub as a global coding community. If you’re looking for GitHub-related projects, exploring Yexex.GitHub could be worth your time!
-

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoRise and Fall of Realm Scans: Exploring Paranormal Mysteries
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoMisty Severi – The Breaking News Reporter
-

 Technology1 year ago
Technology1 year agoIntegremos, What is it? Complete Information
-

 Education1 year ago
Education1 year agoMyOLSD: A Guide to Login, Portals & Resources
-
 Business1 year ago
Business1 year agoPaycor Company: Details, Login & Recruitment
-

 Business1 year ago
Business1 year agoHow to Recruit New Employees?
-

 World1 year ago
World1 year agoTrump Nominated for Nobel Peace Prize Over Abraham Accords
-

 World1 year ago
World1 year agoTrulife Distribution Lawsuit: A Scandal Regarding Health & Wellbeing
















